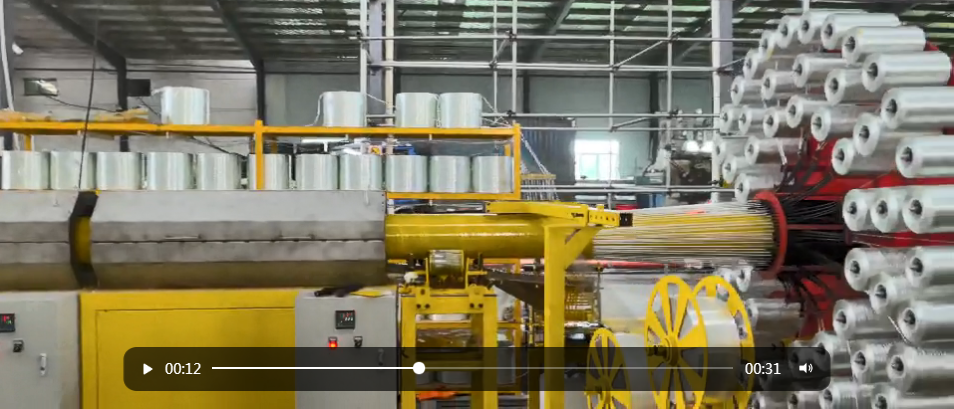
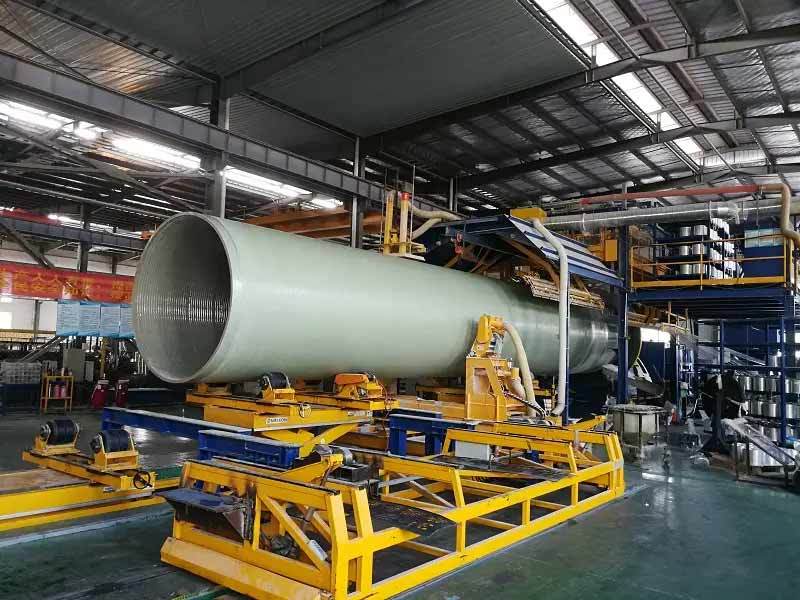
The Future of Manufacturing: How GRP Plants Are Revolutionizing the Industry
Mar 20,2025
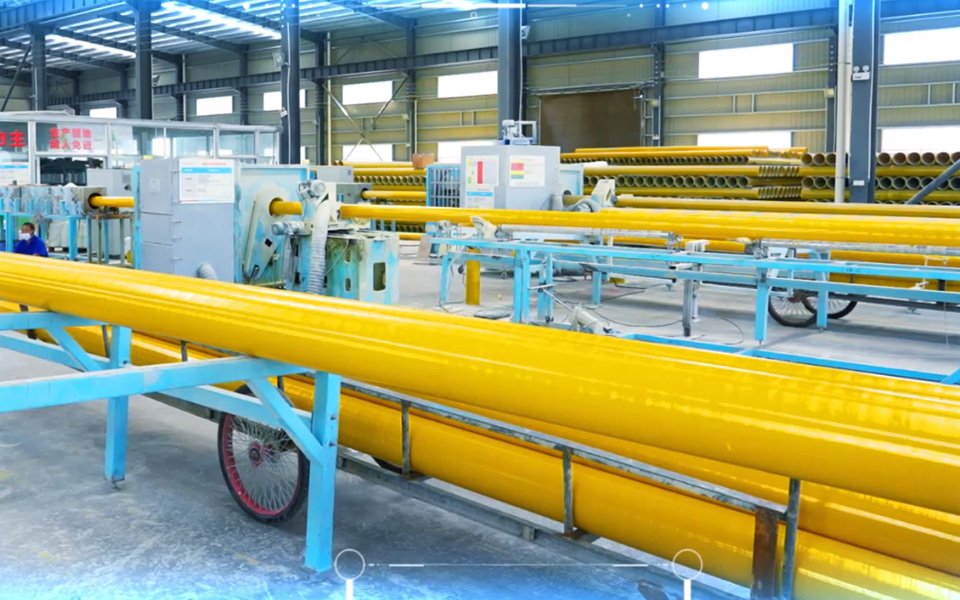

The Future of Manufacturing: How GRP Plants Are Revolutionizing the Industry
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to GRP Manufacturing
- 2. What is Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP)?
- 3. A Brief History of GRP in Manufacturing
- 4. Advantages of GRP in Manufacturing
- 5. Diverse Applications of GRP Plants
- 6. Sustainability and Environmental Impact of GRP
- 7. Future Trends in GRP Manufacturing
- 8. Conclusion
- 9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Introduction to GRP Manufacturing
In recent years, the manufacturing industry has witnessed a significant transformation, largely driven by advancements in materials science. Among these advancements, **Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP)** has emerged as a game-changing material that is revolutionizing how products are designed and produced. GRP plants are at the center of this transformation, enabling manufacturers to create strong, lightweight, and versatile products that meet the demands of modern consumers and industries. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of GRP manufacturing, its advantages, diverse applications, and future trends.
2. What is Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP)?
Glass Reinforced Plastic, commonly referred to as **GRP**, is a composite material made from a polymer matrix reinforced with glass fibers. This combination results in a material that is not only lightweight but also exceptionally strong and durable. GRP is known for its versatility, being moldable into various shapes and sizes, making it suitable for a wide range of applications across different industries.
3. A Brief History of GRP in Manufacturing
The roots of GRP manufacturing can be traced back to the early 20th century when engineers began experimenting with reinforced plastics. However, it wasn't until the 1940s that GRP gained widespread recognition, particularly in the aerospace industry. Its lightweight and robust nature made it an ideal choice for aircraft components.
Over the decades, the technology surrounding GRP production has advanced significantly. Today, GRP plants employ cutting-edge techniques, including automated manufacturing processes and advanced curing technologies, to produce high-quality products efficiently.
4. Advantages of GRP in Manufacturing
4.1 Lightweight Yet Durable
One of the standout features of GRP is its **lightweight nature**. Compared to traditional materials like metal and wood, GRP components can significantly reduce the overall weight of products, which is particularly crucial in sectors such as automotive and aerospace. Despite its lightness, GRP boasts impressive strength, allowing it to withstand significant stress and strain.
4.2 Corrosion Resistance
GRP is inherently resistant to corrosion, making it an ideal choice for applications in harsh environments, such as chemical processing and marine applications. This resistance to deterioration ensures a longer lifespan for GRP products, reducing maintenance costs and improving overall efficiency.
4.3 Cost-Effective Solutions
The production of GRP can be more cost-effective than traditional materials in the long run. While the initial investment in GRP manufacturing may be higher, the durability and lower maintenance costs associated with GRP products often lead to significant savings over time. This cost-effectiveness is especially appealing to industries looking to optimize their budgets without sacrificing quality.
5. Diverse Applications of GRP Plants
The versatility of GRP has led to its adoption in various industries. Below, we explore some of the most common applications of GRP plants.
5.1 GRP in Construction
In the construction industry, GRP is used for a variety of applications, including roofing, cladding, and structural components. Its lightweight nature allows for easier handling and installation, while its strength ensures structural integrity. Additionally, GRP's resistance to weathering makes it a preferred choice for outdoor applications.
5.2 GRP in Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has increasingly turned to GRP for manufacturing components such as body panels, interiors, and structural elements. By incorporating GRP into vehicles, manufacturers can achieve **fuel efficiency** through weight reduction while maintaining safety standards. Moreover, GRP allows for greater design flexibility, enabling more innovative vehicle designs.
5.3 GRP in Marine Applications
GRP is extensively used in the marine sector, particularly for boat hulls and components. Its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties make it ideal for manufacturing durable marine vessels that can withstand harsh ocean conditions. GRP boats not only offer enhanced performance but also require less maintenance compared to traditional materials.
6. Sustainability and Environmental Impact of GRP
As industries worldwide strive for sustainability, GRP manufacturing presents several opportunities for reducing environmental impact. The lightweight nature of GRP contributes to fuel savings in transport, while its durability means fewer resources are required for replacements and repairs. Additionally, advances in recycling technologies are making it possible to reclaim and reuse GRP materials, further enhancing its eco-friendly profile.
7. Future Trends in GRP Manufacturing
The future of GRP manufacturing looks promising, with several trends shaping its evolution:
1. **Advanced Manufacturing Techniques**: The introduction of automation and robotics in GRP production is expected to increase efficiency and precision, reducing production times and costs.
2. **Smart GRP Materials**: Researchers are exploring the integration of smart technologies into GRP materials, allowing for real-time monitoring and self-repair capabilities.
3. **Increased Recycling Efforts**: As environmental concerns grow, the focus on recycling GRP materials will intensify, leading to more sustainable production practices.
4. **Customization and Design Innovation**: The ability to create complex shapes and designs will continue to drive innovation in various industries, enabling the development of tailored solutions that meet specific needs.
8. Conclusion
In summary, Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP) plants are revolutionizing the manufacturing industry through their innovative applications and numerous advantages. As we continue to embrace sustainability and advanced manufacturing techniques, GRP is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of various sectors. By leveraging the unique properties of GRP, manufacturers can create products that are not only high in quality but also environmentally friendly, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient manufacturing landscape.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the primary benefits of using GRP over traditional materials?
The primary benefits of GRP include its lightweight nature, high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness in the long run.
2. Can GRP be recycled?
Yes, advances in recycling technologies are making it possible to reclaim and reuse GRP materials, contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing process.
3. What industries utilize GRP manufacturing?
GRP manufacturing is utilized across various industries, including construction, automotive, and marine sectors.
4. How does GRP contribute to sustainability?
GRP contributes to sustainability through reduced weight in transportation, longer product lifespans, and the potential for recycling, minimizing resource consumption.
5. What future trends are emerging in GRP manufacturing?
Emerging trends include advanced manufacturing techniques, the integration of smart technologies, increased recycling efforts, and innovation in customization and design.
PREVIOUS:
Contact Us
E-mail:
Phone/Wechat/WhatsApp
Address:
A2-1408, Kaichuang Avenue to Tai Plaza, Huangpu District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province