Understanding the Different Types of Filament Winding Machines Available Today
Jul 29,2025
Understanding the Different Types of Filament Winding Machines Available Today
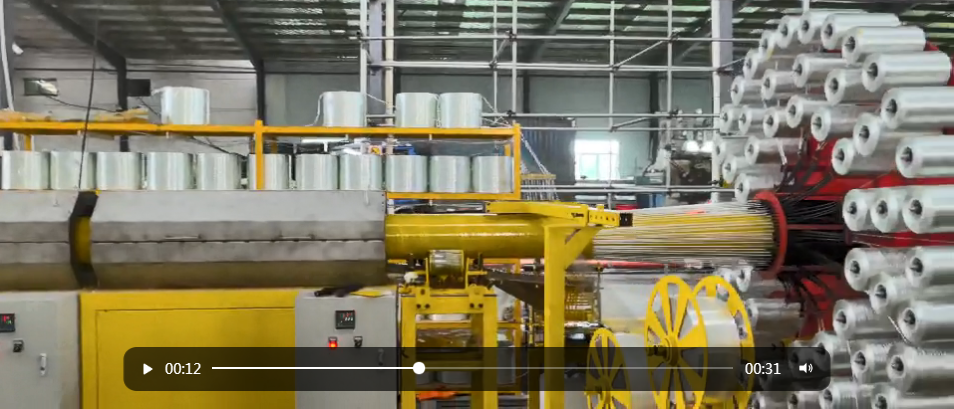
Filament winding is a highly efficient process used in the production of composite materials, particularly in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and marine. The technology involves winding continuous strands of fiber around a mandrel to create a composite structure that is both strong and lightweight. In this article, we will explore the different types of filament winding machines available today, their applications, and the advantages they offer in various manufacturing processes.
Table of Contents
- What is Filament Winding?
- Types of Filament Winding Machines
- Manual Filament Winding Machines
- Semi-Automatic Filament Winding Machines
- Fully Automatic Filament Winding Machines
- Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machines
- Applications of Filament Winding Machines
- Advantages of Filament Winding
- Choosing the Right Filament Winding Machine
- Common Issues and Solutions
- The Future of Filament Winding Technology
- FAQs on Filament Winding Machines
What is Filament Winding?
Filament winding is a manufacturing process that involves the application of filaments—typically made of glass or carbon fiber—around a rotating mandrel. This technique allows for the production of high-strength composite parts, which are commonly used in industries requiring lightweight yet durable materials. The process can create a variety of shapes, including cylindrical, conical, and complex geometries, making it highly versatile.
Types of Filament Winding Machines
Several types of filament winding machines are available, each catering to specific manufacturing needs. Understanding these types will help businesses select the right equipment for their applications.
Manual Filament Winding Machines
Manual filament winding machines are operated by skilled technicians who control the winding process. These machines are often less expensive than automated options and are suitable for small-scale production runs or prototyping. While they allow for high levels of customization, they may not achieve the same consistency and speed as automated machines.
Semi-Automatic Filament Winding Machines
Semi-automatic filament winding machines combine manual operation with automated features. Operators still play a crucial role, but certain processes, such as the mandrel rotation and fiber tension control, are automated. This balance enhances productivity while maintaining flexibility in design. These machines are ideal for medium-scale production where a mix of customization and efficiency is needed.
Fully Automatic Filament Winding Machines
Fully automatic filament winding machines are designed for high-volume production. These systems handle all aspects of the winding process, including fiber placement, tension control, and mandrel rotation. By maximizing efficiency and reducing labor costs, fully automatic machines are favored by large manufacturers seeking to produce high-quality composite parts at scale.
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machines
CNC filament winding machines represent the pinnacle of technology in this field. These machines use advanced software to control the winding process precisely, allowing for intricate patterns and designs that would be difficult to achieve manually. CNC machines offer superior accuracy, repeatability, and the ability to produce complex geometries, making them ideal for specialized applications in aerospace and medical industries.
Applications of Filament Winding Machines
Filament winding machines are used across various industries due to their ability to create strong and lightweight composite materials. Some of the primary applications include:
Aerospace
In the aerospace sector, filament winding is used to manufacture components such as fuel tanks, airframe structures, and rotor blades. The lightweight nature of composites helps reduce overall aircraft weight, improving fuel efficiency and performance.
Automotive
The automotive industry employs filament winding technology to produce components like drive shafts, pressure vessels, and lightweight structural parts. These applications benefit from the strength-to-weight ratio of composites, leading to enhanced performance and reduced emissions.
Marine
Composite materials created using filament winding are ideal for marine applications, including boat hulls and masts. The corrosion resistance and structural integrity of these materials make them well-suited for the harsh marine environment.
Industrial Equipment
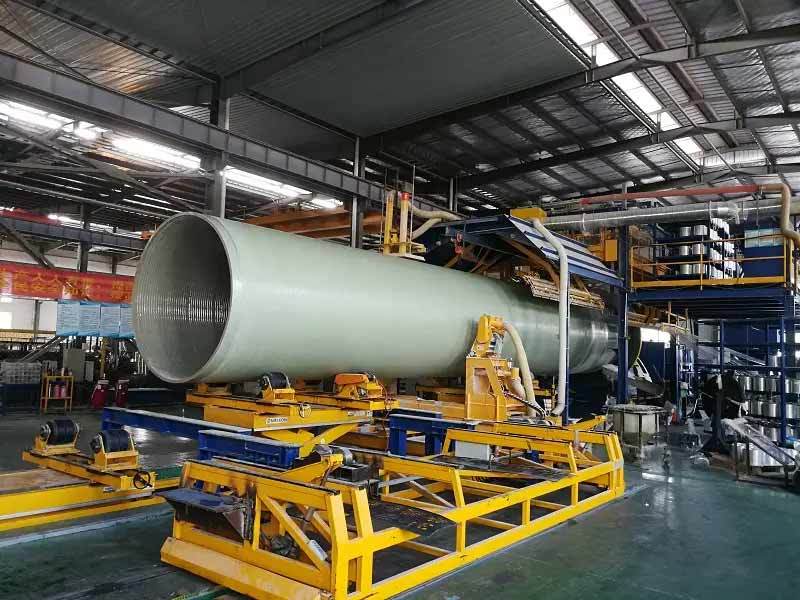
Filament winding machines are also used to manufacture industrial components such as pipes, tanks, and pressure vessels. The durability and strength of composite materials make them a preferred choice for demanding industrial applications.
Advantages of Filament Winding
The benefits of using filament winding technology are numerous, making it an attractive option for manufacturers. Key advantages include:
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Composite materials produced through filament winding exhibit exceptional strength while remaining lightweight. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in industries where weight reduction is critical.
Design Flexibility
Filament winding allows for the creation of complex geometries and customized designs, enabling manufacturers to meet specific performance requirements and design criteria.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in filament winding machines can be significant, the long-term cost savings associated with reduced material waste and labor costs often justify the expense.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Composite materials are inherently resistant to corrosion and environmental degradation, making them suitable for applications in harsh conditions.
Choosing the Right Filament Winding Machine
Selecting the appropriate filament winding machine depends on various factors, including production volume, material type, and desired part complexity. Here are some considerations to help guide your decision:
Production Volume
Evaluate your expected production volume to determine whether a manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic machine is the best fit. Higher production volumes typically warrant investing in more automated systems.
Material Compatibility
Consider the types of fibers and resin systems you will be using. Different filament winding machines are optimized for specific materials, so ensure your chosen machine aligns with your material requirements.
Complexity of Design
For intricate designs, CNC machines may be necessary to achieve the precision needed. Assess your design requirements and choose a machine that can handle the complexity.
Common Issues and Solutions
While filament winding technology offers numerous advantages, it is not without challenges. Understanding common issues can help improve efficiency and reduce downtime.
Tension Management
Inconsistent fiber tension can lead to defects in the final product. Implementing automatic tension control systems can help maintain consistent tension throughout the winding process.
Surface Defects
Surface imperfections can occur during winding, impacting the quality of the composite part. Regular maintenance and quality checks can help identify and resolve issues before they affect production.
Curing Issues
Improper curing of resin can result in weak or compromised parts. Ensure that the curing process is closely monitored and adjusted as needed to achieve optimal results.
The Future of Filament Winding Technology
The filament winding industry is evolving rapidly, with advancements in technology and materials driving innovation. Future trends may include:
Smart Manufacturing
The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology will enable manufacturers to monitor machine performance and production metrics in real-time, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime.
Advanced Materials
Research into new composite materials is ongoing, with the potential for lighter and stronger fibers that can further enhance the performance of filament-wound products.
Sustainability Initiatives
As industries move toward more sustainable practices, the development of eco-friendly resin systems and recycling methods for composite materials will become increasingly important.
FAQs on Filament Winding Machines
1. What materials can be used in filament winding?
Filament winding commonly uses materials like glass fiber, carbon fiber, and aramid fiber, combined with thermosetting or thermoplastic resins.
2. How does filament winding compare to other composite manufacturing processes?
Filament winding offers superior strength-to-weight ratios and design flexibility compared to processes like layup or resin transfer molding.
3. What are the maintenance requirements for filament winding machines?
Regular maintenance includes checking for wear on moving parts, ensuring proper lubrication, and monitoring the calibration of tension control systems.
4. Can filament winding machines be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor machines for specific materials, designs, and production processes.
5. What is the cost range for filament winding machines?
Costs vary significantly based on machine type and features, ranging from a few thousand dollars for manual machines to hundreds of thousands for advanced CNC systems.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of filament winding machines available today is essential for manufacturers looking to optimize their production processes. Each machine type, from manual to fully automatic, offers unique advantages and applications. By evaluating your specific needs and considering the benefits of filament winding technology, you can make informed decisions that enhance productivity and product quality in your manufacturing operations. As the industry continues to evolve, staying abreast of advancements and trends will ensure that your business remains competitive in the dynamic landscape of composite manufacturing.
PREVIOUS:
Contact Us
E-mail:
Phone/Wechat/WhatsApp
Address:
A2-1408, Kaichuang Avenue to Tai Plaza, Huangpu District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province