Exploring the Key Features of Advanced GRP Plants: A Comprehensive Guide
Apr 03,2025

Exploring the Key Features of Advanced GRP Plants
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to GRP Plants
- 2. What is Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP)?
- 3. Significance of GRP in Modern Manufacturing
- 4. Key Features of Advanced GRP Plants
- 4.1 Automated Manufacturing Process
- 4.2 High-Performance Materials
- 4.3 Sustainability Initiatives
- 4.4 Flexible Manufacturing Systems
- 4.5 Quality Control Measures
- 5. Case Studies of Successful GRP Plants
- 6. Future Trends in GRP Manufacturing
- 7. FAQs About GRP Plants
- 8. Conclusion
1. Introduction to GRP Plants
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing technologies, **Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP)** plants have emerged as a beacon of innovation and efficiency. The advanced capabilities of these plants not only revolutionize how products are manufactured but also enhance the overall performance and sustainability of materials used. This article delves into the essential features that define modern GRP plants, illustrating their crucial role in various industries.
2. What is Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP)?
**Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP)**, also known as fiberglass, is a composite material made of a polymer matrix reinforced with glass fibers. This combination results in a lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant material ideal for various applications, including construction, automotive, and aerospace industries. The versatility of GRP stems from its unique properties, making it a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking durable and efficient materials.
3. Significance of GRP in Modern Manufacturing
The significance of GRP in modern manufacturing cannot be overstated. Its favorable strength-to-weight ratio allows manufacturers to design products that are both robust and lightweight. Furthermore, GRP's resistance to moisture and chemicals makes it an ideal material for outdoor applications and environments where exposure to harsh conditions is prevalent. As industries move towards more sustainable practices, the recyclable nature of GRP adds to its appeal.
4. Key Features of Advanced GRP Plants
The characteristics of advanced GRP plants are crucial in determining their efficiency and effectiveness. Below are some of the notable features that set these plants apart.
4.1 Automated Manufacturing Process
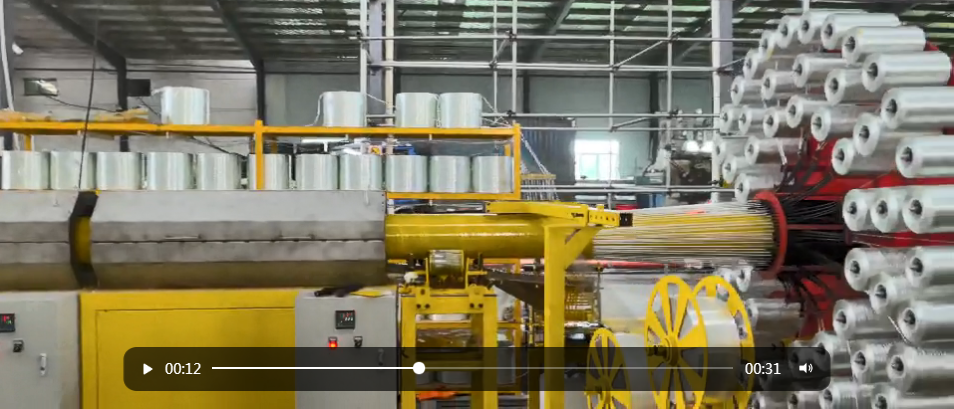
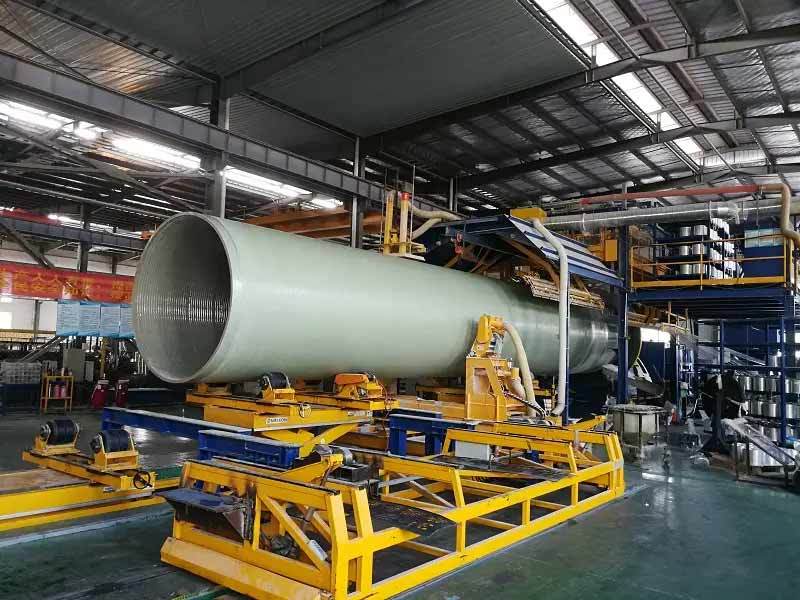
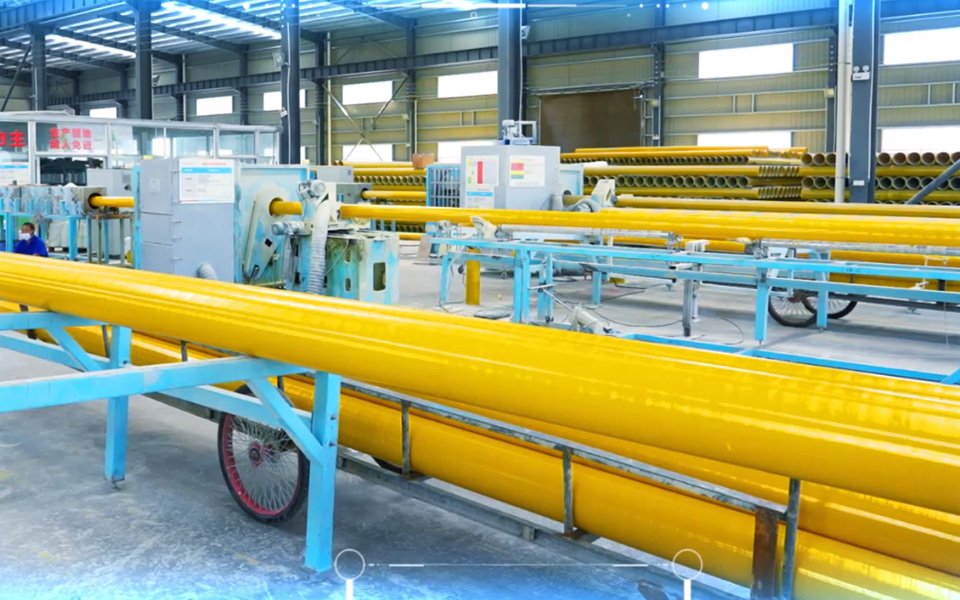
Automation stands at the forefront of advanced GRP plants. Implementing **automated manufacturing processes** significantly reduces human error while increasing productivity and consistency. These systems utilize robotics and computer-controlled machinery to perform tasks such as fiberglass layup, curing, and finishing. The result is a streamlined production flow that enhances operational efficiency.
4.2 High-Performance Materials
Advanced GRP plants employ high-performance materials that provide superior mechanical properties and longevity. These materials are designed to withstand extreme conditions, such as high temperatures and corrosive environments. By utilizing advanced resins and reinforcement techniques, manufacturers can produce GRP components that meet strict industry standards, ensuring safety and reliability.
4.3 Sustainability Initiatives
Sustainability is a crucial consideration in modern manufacturing processes. Advanced GRP plants adopt various **sustainability initiatives** aimed at reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact. These initiatives include recycling excess materials, using eco-friendly resins, and implementing energy-efficient production techniques. Such measures not only comply with regulations but also appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
4.4 Flexible Manufacturing Systems
The ability to adapt quickly to market demands is essential for any manufacturing business. Advanced GRP plants feature **flexible manufacturing systems** that allow for rapid adjustments in production schedules and product designs. This flexibility enables manufacturers to respond promptly to customer needs, thus maintaining a competitive edge in the dynamic market.
4.5 Quality Control Measures
Ensuring the quality of GRP products is paramount. Advanced GRP plants employ stringent **quality control measures** at every stage of production. From raw material selection to the final inspection of finished products, quality assurance processes are meticulously followed. Utilizing advanced testing methods, such as non-destructive testing and material characterization, manufacturers can guarantee that their products meet or exceed industry standards.
5. Case Studies of Successful GRP Plants
Examining real-world examples of advanced GRP plants provides insight into how these features are implemented effectively. For instance, a leading manufacturer in the automotive industry integrated automated processes and high-performance materials to enhance the production of lightweight vehicle components. This innovation not only reduced manufacturing costs but also improved fuel efficiency for the end products.
Another example can be found in the construction sector, where a GRP plant adopted sustainability initiatives that significantly cut down on waste. By recycling previous batches of GRP materials, they achieved a notable reduction in raw material consumption while maintaining product quality.
6. Future Trends in GRP Manufacturing
As technology continues to advance, the future of GRP manufacturing looks promising. Key trends anticipated in the industry include the integration of **smart technologies** in production lines, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies will allow for real-time monitoring and optimization of manufacturing processes, leading to even greater efficiency and reduced costs.
Another trend is the increased focus on **biodegradable and recyclable materials**, driven by consumer demand for sustainable products. As manufacturers explore innovative resin formulations, the potential for more environmentally friendly options is expanding.
7. FAQs About GRP Plants
What are the main advantages of using GRP in manufacturing?
GRP offers numerous advantages, including its lightweight nature, high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and versatility in design applications.
How are advanced GRP plants different from traditional manufacturing facilities?
Advanced GRP plants utilize automation, high-performance materials, and sustainable practices, whereas traditional facilities may rely more on manual labor and outdated processes.
What industries benefit from GRP manufacturing?
GRP manufacturing serves various industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, marine, and consumer goods, due to its adaptability and performance characteristics.
How do sustainability initiatives in GRP plants reduce environmental impact?
Sustainability initiatives, including recycling and using eco-friendly materials, help reduce waste and lower the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes.
What role does quality control play in GRP production?
Quality control is essential in GRP production to ensure that materials meet industry standards, thus guaranteeing the safety and reliability of the final products.
8. Conclusion
In summary, advanced GRP plants represent a significant leap forward in manufacturing technology. Their combination of automation, high-performance materials, sustainability initiatives, and stringent quality control measures positions them as leaders in the industry. As we look to the future, the continued evolution of GRP manufacturing will undoubtedly yield innovative solutions that meet the demands of a rapidly changing market. Understanding these key features will not only aid industry professionals but also empower consumers to make informed choices about the products they use in their daily lives.
Contact Us
E-mail:
Phone/Wechat/WhatsApp
Address:
A2-1408, Kaichuang Avenue to Tai Plaza, Huangpu District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province