Understanding GRP Plants: Innovations in Manufacturing Processes
Apr 10,2025

---
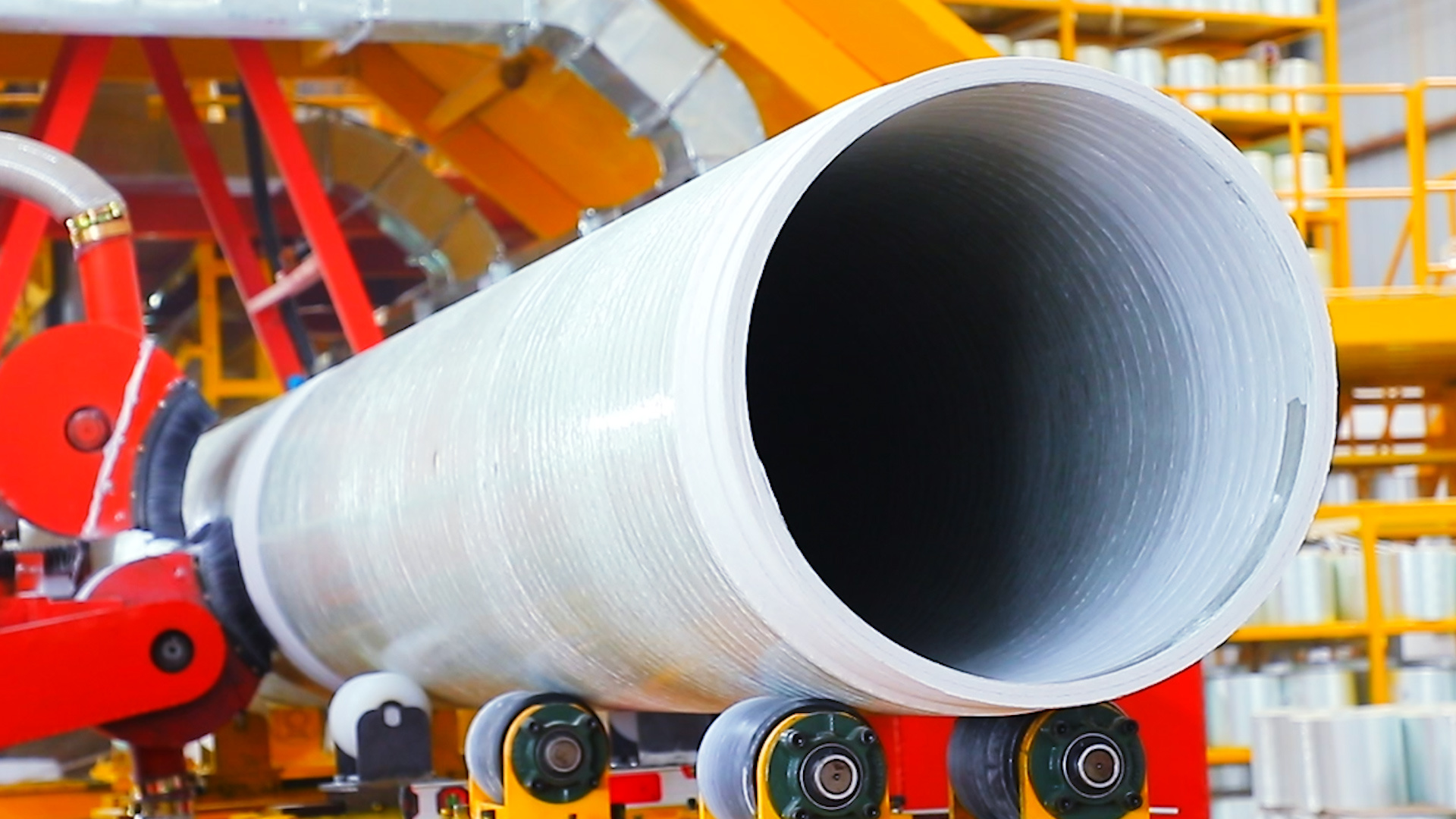
In the realm of manufacturing, particularly within the sector of advanced processing machinery, GRP plants play a pivotal role. GRP, or Glass Reinforced Plastic, is a composite material made from a polymer matrix reinforced with glass fibers. This combination results in a lightweight, yet robust material that has become increasingly popular across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction.
One of the primary advantages of GRP materials is their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. This characteristic makes them ideal for applications where reducing weight is crucial without compromising structural integrity. For example, in the automotive industry, manufacturers are continually seeking ways to improve fuel efficiency by decreasing the weight of vehicles. GRP components provide a viable solution, enabling manufacturers to create lighter vehicles without sacrificing safety or durability.
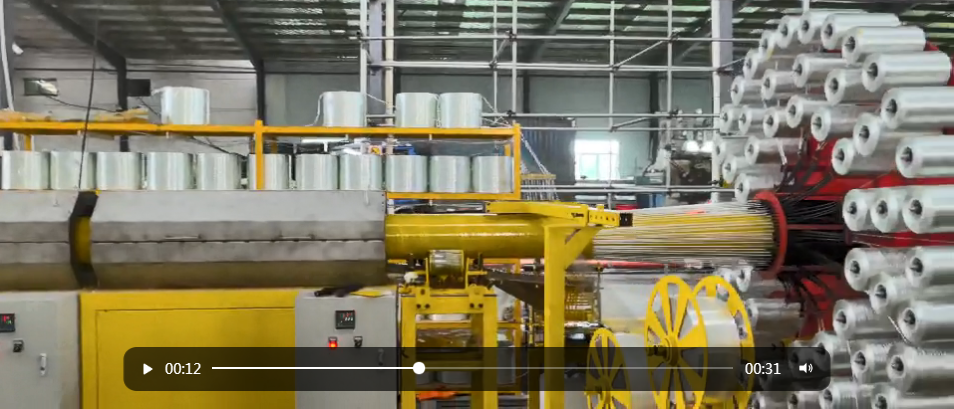
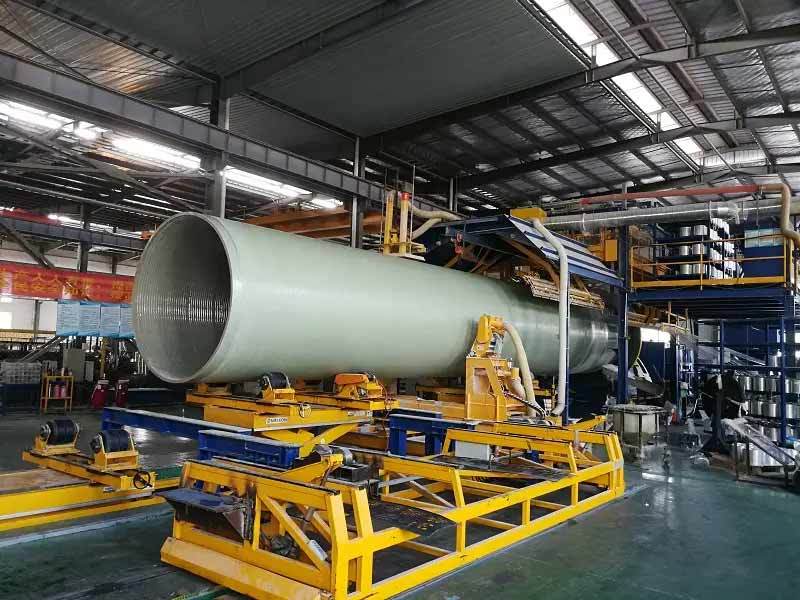
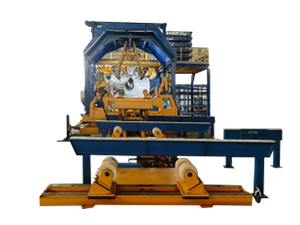
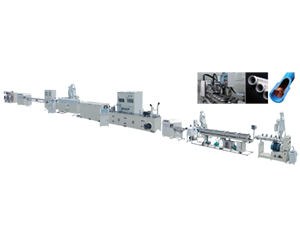
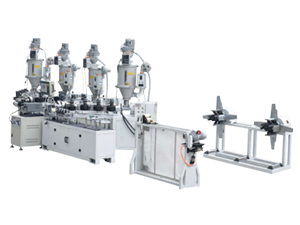
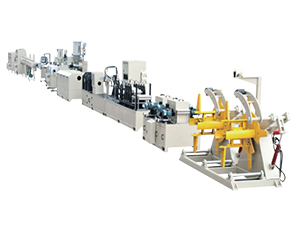
A GRP plant is specifically designed to produce components using this innovative material. The manufacturing process typically involves several key stages, including the preparation of raw materials, the molding of components, and the curing process. Understanding these stages can provide valuable insights into how GRP plants operate and how they can enhance production efficiency.
The preparation stage involves selecting and mixing the appropriate resin and glass fibers. The choice of materials is critical, as it influences the final product's properties. Once the mixture is prepared, it is transferred to the molding stage, where it is shaped into the desired form using molds. This can include various techniques such as hand lay-up, spray-up, or resin transfer molding, each suitable for different applications and production scales.
After molding, the components undergo a curing process, where the resin hardens and bonds with the glass fibers, resulting in a strong and durable product. This stage is crucial, as it determines the final product's overall strength and performance characteristics.
Moreover, GRP plants are continuously evolving to incorporate advanced technologies such as automation and precision engineering. These innovations not only enhance product quality but also optimize production processes, ensuring that manufacturers can meet the growing demands of their markets.
In conclusion, GRP plants represent a significant advancement in the manufacturing and processing machinery sector. By leveraging the unique properties of Glass Reinforced Plastic, these facilities provide manufacturers with the tools they need to produce lightweight, durable, and efficient products. As industries continue to innovate and push the boundaries of traditional manufacturing, understanding the role of GRP plants will become increasingly important for professionals in the field.
In the realm of manufacturing, particularly within the sector of advanced processing machinery, GRP plants play a pivotal role. GRP, or Glass Reinforced Plastic, is a composite material made from a polymer matrix reinforced with glass fibers. This combination results in a lightweight, yet robust material that has become increasingly popular across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction.
One of the primary advantages of GRP materials is their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. This characteristic makes them ideal for applications where reducing weight is crucial without compromising structural integrity. For example, in the automotive industry, manufacturers are continually seeking ways to improve fuel efficiency by decreasing the weight of vehicles. GRP components provide a viable solution, enabling manufacturers to create lighter vehicles without sacrificing safety or durability.
A GRP plant is specifically designed to produce components using this innovative material. The manufacturing process typically involves several key stages, including the preparation of raw materials, the molding of components, and the curing process. Understanding these stages can provide valuable insights into how GRP plants operate and how they can enhance production efficiency.
The preparation stage involves selecting and mixing the appropriate resin and glass fibers. The choice of materials is critical, as it influences the final product's properties. Once the mixture is prepared, it is transferred to the molding stage, where it is shaped into the desired form using molds. This can include various techniques such as hand lay-up, spray-up, or resin transfer molding, each suitable for different applications and production scales.
After molding, the components undergo a curing process, where the resin hardens and bonds with the glass fibers, resulting in a strong and durable product. This stage is crucial, as it determines the final product's overall strength and performance characteristics.
Moreover, GRP plants are continuously evolving to incorporate advanced technologies such as automation and precision engineering. These innovations not only enhance product quality but also optimize production processes, ensuring that manufacturers can meet the growing demands of their markets.
In conclusion, GRP plants represent a significant advancement in the manufacturing and processing machinery sector. By leveraging the unique properties of Glass Reinforced Plastic, these facilities provide manufacturers with the tools they need to produce lightweight, durable, and efficient products. As industries continue to innovate and push the boundaries of traditional manufacturing, understanding the role of GRP plants will become increasingly important for professionals in the field.
PREVIOUS:
Contact Us
E-mail:
Phone/Wechat/WhatsApp
Address:
A2-1408, Kaichuang Avenue to Tai Plaza, Huangpu District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province